Understanding lipomas and their removal options is crucial for anyone dealing with these common fatty lumps. Whether you’re in Glasgow or simply seeking information about lipoma removal, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything from diagnosis to treatment options, helping you make informed decisions about your health care.
Lipoma Removal in Glasgow
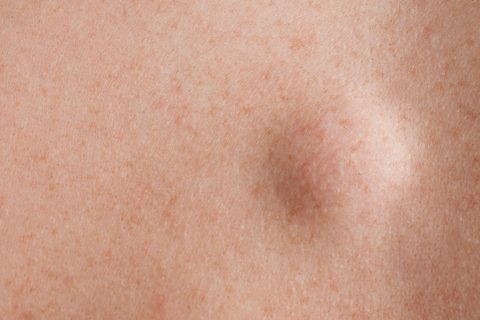
Find Out More About Lipoma Removal at Our Glasgow Clinic
What Exactly Is a Lipoma and How Can You Identify One?
A lipoma is a benign, slow-growing fatty lump that develops underneath the skin. Lipomas are typically found on the abdomen, back, shoulders, or arms, but they can appear almost anywhere on the body. Lipomas are generally harmless and do not require treatment unless they are causing discomfort, growing rapidly, or are cosmetically concerning. Lipomas are soft, smooth, and easily movable. They are composed of fat tissue and are not cancerous.
Lipomas are usually small, but they can grow larger over time. While the exact cause of lipomas is unknown, some research suggests a genetic link, particularly in a condition called familial multiple lipomatosis, where individuals develop multiple lipomas. Lipomas are not related to other skin condition such as acne.
Why Might You Need Lipoma Removal in Glasgow?
While lipomas are harmless, there are several reasons why you might consider having them removed. Some patients seek treatment to remove lipomas for cosmetic reasons, while others experience discomfort when the lipoma is squeezed or pressed. In certain cases, the size of the lipoma may interfere with daily activities or cause anxiety about appearance.
The decision to pursue lipoma removal often comes after consultation with a GP or specialist. During these consultations, medical professionals can assess whether the growth requires treatment and discuss various treatment options available.
-
I had an appointment with Dr Fraser today at the skin clinic. She was excellent and dealt with all my issues in one appointment with no need for any follow up. Lovely staff to welcome you in the door too. I will definitely go back for any future treatments if needed and thoroughly recommend Dr Fraser for her kindness too.
-
I went to to the doctor to have a small growth on my back checked. After being reassured it was bleeding because it was catching on my clothing, annoying not sinister, i was offered the opportunity to have it removed at the surgery. It was duly removed one week later in a painless procedure in a calm environment. Highly recommend.
-
I was referred to Waverley Park by my GP to address a cyst on my back and spot on my face. Dr Fraser evaluated both and treated the spot on my cheek, which resolved within a week. I returned to have the cyst surgically removed and was seen promptly. The procedure was quick and fairly painless and the staff were kind. Highly recommend Waverley Park and Dr Fraser for minor surgical procedures.
Understanding Different Types of Lesions: Cyst, Mole, and Skin Tag
Besides lipomas, other common skin lesions include cysts, moles, and skin tags. A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can develop under the skin. Moles are pigmented spots on the skin, while skin tags are small, soft growths of skin that hang off the body by a connecting stalk. It is important to differentiate between these lesions and a lipoma as the treatment options may vary.
What Should You Expect During Your Initial Consultation?
Your initial consultation typically involves a physical examination of the lesion, a review of your medical history, and a discussion of treatment options. The doctor will assess the lipoma, determine if any further tests, such as an ultrasound scan, may be necessary, and explain the surgical excision procedure in detail. The doctor will discuss the benefits and risks of lipoma removal and help you make an informed decision.
How Is the Surgical Procedure Performed?
Surgical excision is the most common method for lipoma removal. The procedure is performed using local anaesthetic, which numbs the area around the lipoma. A small incision is made in the skin, and the lipoma is carefully dissected and removed. The wound is then closed with sutures. The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes, depending on the size and location of the lipoma.
Special attention is paid to minimize scarring, and the wound is carefully closed to promote optimal healing. The removed tissue will be sent to our local pathology lab for confirmation of the diagnosis and we will notify your GP of the result.
Is NHS Treatment Available for Lipoma Removal?
While the NHS does provide lipoma removal services in certain circumstances, there may be waiting times, especially if the lipoma is considered a cosmetic concern rather than a medical necessity. Your GP can advise whether NHS treatment is appropriate for your situation.
Lipoma Removal Cost
The fee for your initial consultation is £50. We are pleased to deduct this amount entirely from the cost of any subsequent procedures you choose to pursue.
Key Points to Remember:
- Lipomas are non-cancerous, slow-growing fatty lumps that grow under your skin
- Professional medical consultation is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning
- Surgical excision is the most common and effective method for lipoma removal.
- Proper aftercare is essential following lipoma removal to minimise the risk of infection and promote healing.
